by Kathy B. Lauder.
Although City Cemetery, Nashville’s first public burial ground (1822) accepted people of all races from the beginning, the rise of the “Jim Crow” South after the Civil War compelled African Americans to look elsewhere for a final resting place. In 1869 black businessman Nelson Walker and the Colored Benevolent Society bought land for Mt. Ararat Cemetery near the Elm Hill-Murfreesboro Pike intersection, directly behind today’s Purity Dairy plant. Walker (1825-1875), a barber at the Maxwell House, became an important figure in African American politics after the Civil War. Elected president of the first State Colored Men’s Convention (August 1865), he was active in the Masonic Order, the Sons of Relief, and the State Colored Emigration Board. Largely self-educated, he became a practicing attorney and later a Davidson County magistrate. An outspoken supporter of the public schools, Walker encouraged his seven children to become well educated – his daughter Virginia was a member of Fisk University’s first graduating class in 1875.

When Mt. Ararat burial plots went on sale in May 1869, church leaders urged their parishioners to purchase them. Mt. Ararat received considerable media attention in 1890 when Reverend Nelson Merry’s remains were reinterred there from City Cemetery, and again in 1892, after three heroic African American firemen lost their lives fighting a devastating fire in downtown Nashville. The day of their burial was declared a city-wide day of mourning, and the procession leading from their funeral ceremony at the Capitol to the cemetery was said to be over a mile long. Mt. Ararat (now Greenwood West) became part of the Greenwood Cemetery complex in 1982.
Another key figure in Nashville history was the Reverend Preston Taylor (1849-1931). Born into slavery, he served as a Union Army drummer boy when he was a young teenager. While still in his 20s he founded a Mt. Sterling, Kentucky, church, attracting the largest congregation in the state during his fifteen years there, while also working as a contractor to build several sections of the Big Sandy Railroad. After moving to Nashville, he preached at the Gay Street Christian church and also joined the Masons and the IOOF, holding state offices in both organizations.
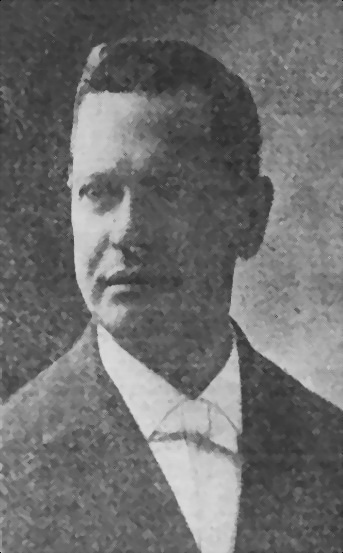
As the 19th century ended, Preston Taylor committed himself to improving the social and economic condition of Nashville’s black community. Already well known as a local religious leader and businessman, he opened the city’s first African American mortuary, the Taylor Funeral Company, in 1888, the same year he and three others came together to purchase land for a “first class burial space . . . available at cost” for African American families. After his partners backed out of the project, Taylor alone funded the purchase of a 37-acre site on Elm Hill Pike and Spence Lane, near Buttermilk Ridge (so-called because of the scattering of dairy farms along the big S-curve on Lebanon Road east of Spence). Greenwood Cemetery, still in operation today, opened in 1888. Preston Taylor’s will deeded the cemetery to the Disciples of Christ religious organization, who continue to operate the facility (now merged with Mt. Ararat/ Greenwood West) as a non-profit enterprise. Preston Taylor is buried beneath a striking monument near the entrance to Greenwood. He was also involved in establishing the Lea Avenue Christian Church, the National Colored Christian Missionary Convention, the One Cent Bank (now Citizens Savings & Trust), and Tennessee State A&I Normal School (now Tennessee State University).

Jim Crow laws barred African Americans not only from cemeteries but also from many entertainment venues. However, in 1905 Preston Taylor responded to these restrictions by opening Greenwood Park north of the cemetery on the large unused portion of his original 37-acre land purchase. The park’s entrance stood just west of the intersection of Lebanon Road and Spence Lane. The first recreational park for Nashville’s black community, its attractions included a merry-go-round, a roller coaster, a shooting gallery, and a skating rink. Visitors could attend events at a baseball park, a bandstand, or a theatre, and if they were hungry, they could eat at a barbecue stand, a lunchroom, or a well-maintained picnic area. The area was spacious enough to include a Boy Scout camp, a racetrack, and a zoo, and it was home to the Colored State Fair, as well as other popular annual celebrations on Labor Day and July 4th. The Barbers’ Union, Masonic Lodges, and USCT veterans scheduled special events in the park. Taylor, who actually lived on the grounds, banned fighting, drinking, or cursing by Greenwood visitors and required them to dress appropriately. When white neighbors complained about Greenwood and its attendant congestion, only Ben Carr’s last-minute appeal to Governor Patterson rescued the park from ruinous legislation. In 1910 a suspicious fire destroyed Greenwood’s large grandstand, but no one was ever charged with the crime. Preston Taylor died in 1931, but the park survived until 1949, superintended by Taylor’s widow.

Benjamin J. Carr (1875-1935) was another remarkable Tennessean, whose concern for his fellow black citizens resulted in the creation of both a second park and a notable educational institution. Born into poverty, Carr grew up working on farms in Trousdale County, Tennessee. He carefully set aside most of his meager earnings (50¢ per day) to purchase his own farm. In time, the frugal young man was able to pay off his mortgage with income from his tobacco crop. Shortly before 1900 Carr came to Nashville, where he was elected porter for the state Supreme Court and became an unexpected friend and ally of Governor Malcolm Patterson (1907-1911), who sent Carr on a lecture tour throughout Middle Tennessee to educate and inspire black farmers. Carr headed the citizens’ organization that brought the Tennessee Agricultural & Industrial State Normal School (Tennessee A&I, known today as Tennessee State University) to Nashville, and he was the school’s first agriculture teacher. He was also the driving force behind the city’s purchase of 34 acres near the college for use as a municipal park. When Mayor Hilary Howse dedicated Nashville’s Hadley Park in 1912, it became the first public park for African Americans in the entire nation.

The name given to Hadley Park is still a matter of some dispute. When Major Eugene C. Lewis (chairman of the Nashville, Chattanooga, & St. Louis Railway and director-general of the 1897 Tennessee Centennial Exposition) named the park, many assumed the title was a tribute to John L. Hadley, a white slave owner whose home plantation became the site of Tennessee State University. However, Lewis may have intended instead to honor Dr. W. A. Hadley (1850-1901), a physician-educator with whom he had worked closely during the Centennial Exposition, and for whom the Hadley School was named. A graduate of Meharry Medical College, Dr. Hadley had taught briefly in Davidson County schools before opening his medical practice. In 1880 he was elected secretary of the newly formed State Medical Association, and in 1883 he was chosen as a delegate to the National Convention of Colored Men at Louisville. He founded the Independent Order of the Immaculates and served on the executive committee (with Major E. C. Lewis) of the 1897 Centennial. After practicing medicine for several years, Hadley returned to teaching. At the time of his death, he was principal of Carter Public School in Nashville.

Adapted from the Greenwood Project.
